Money and the Mechanism of Exchange
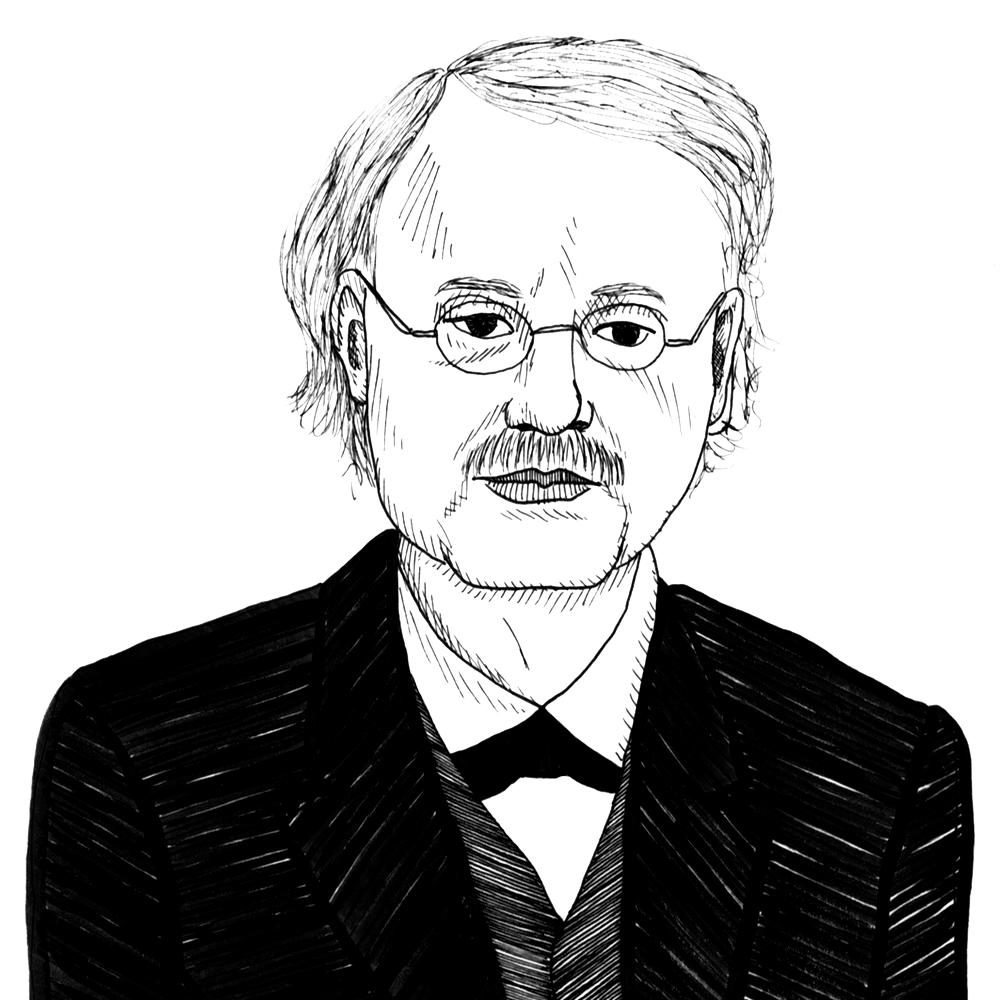
- William Stanley Jevons (author)
Jevons’s formative 1875 classic work came into print at the height of interest in gold, silver, and international monetary standards. Of particular interest are the clear discussions of Gresham’s Law (Ch. VIII), competitively supplied money (Ch. VII), and fractional-reserve- and Free-banking (Ch. XVII-XVIII and XXIV). Jevons is best known for his work on marginal utility, which he describes with customary succinctness in the book.
Related People
Critical Responses

Book
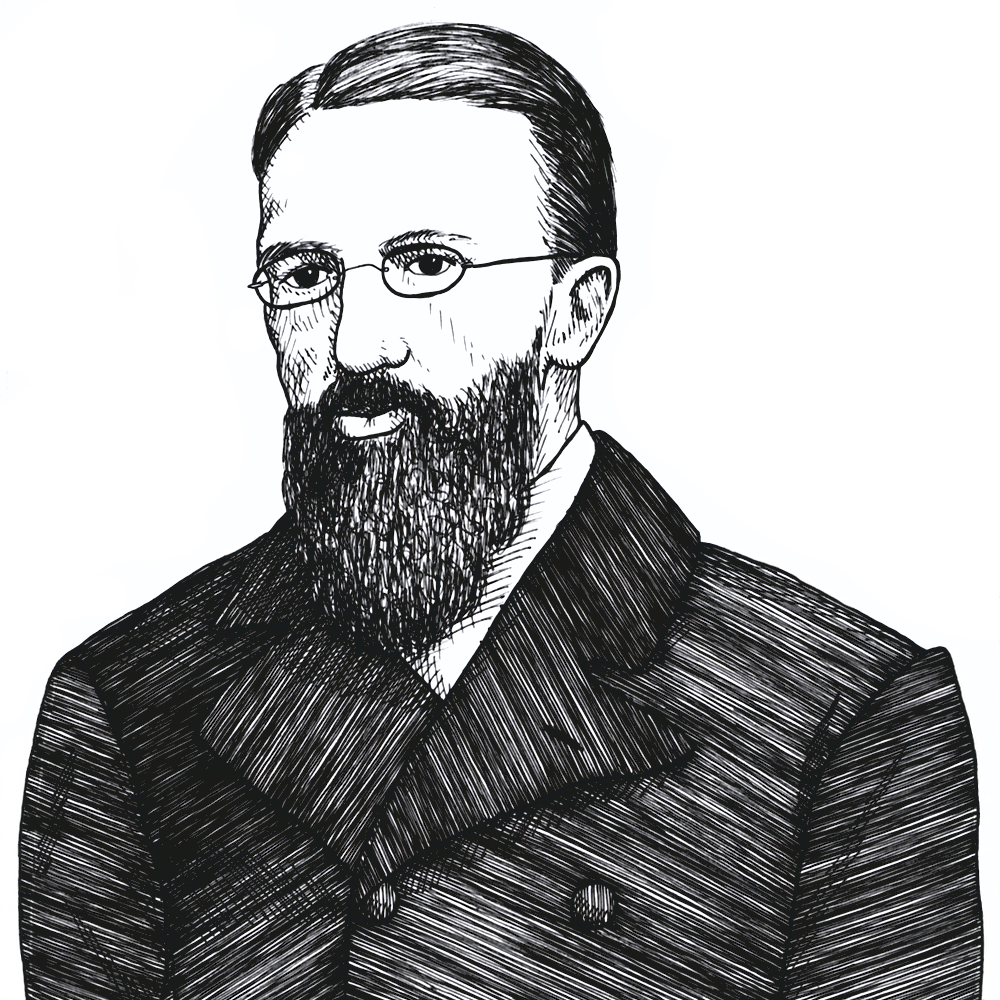
The Origins of MoneyCarl Menger
Menger challenges Jevons’ account of the historical evolution of money by offering a more organic, decentralized model rooted in spontaneous order. While Jevons emphasizes utility and efficiency, Menger stresses emergent institutional development through individual action without centralized…

Book
The Theory of Money and CreditLudwig von Mises
Mises provides a robust critique of earlier monetary theories (including Jevons), offering a praxeological and subjectivist account of money’s value. Mises critiques Jevons for insufficient theoretical depth, especially in the treatment of the demand for money and the role of credit.

Book
The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and MoneyJohn Maynard Keynes
While not direct refutations, Keynes’ theories on money, liquidity preference, and monetary policy mark a sharp departure from Jevons’ equilibrium-centered thinking.

Book
The Denationalization of MoneyFriedrich Hayek
Hayek challenges the very assumptions of state-backed currency systems that underlie parts of Jevons’ analysis. Hayek’s work is a radical rethinking of monetary mechanisms and monetary competition, suggesting limits to centralized monetary design.
Connected Readings